Drones in humanitarian action – at a tipping point?

In December 2016, a consortium led by the Swiss Foundation for Mine Action (FSD) published a major review that provides detailed insight into the use of drones or airbourne systems in humanitarian crises. The review was supported by the EU’s ECHO programme.
Henrike Trautmann, Head of Unit Policy Development and Regional Strategy in the European Commission’s Directorate-General for European Civil Protection and Humanitarian Aid Operations commented:
‘Drones have the potential to be a – literally – small, but important tool to help make disaster response faster and more targeted. The European Commission is supporting its partners in identifying innovations like these and learning from experience so that they become a useful element of humanitarian action’ - Henrike Trautmann.
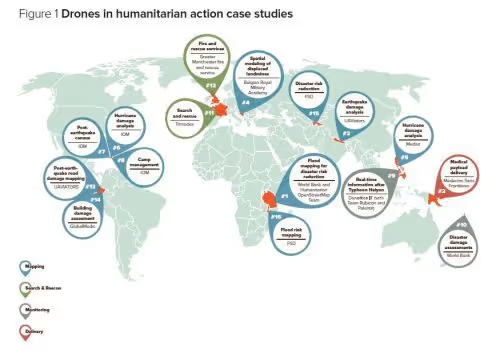
The FSD report focussed on 14 case studies from 10 countries, as well as expert consultations carried out over 2 years. It concluded that mapping was now the most widespread use of drones and has the most immediate humanitarian potential.
However, the authors expect that the ‘considerable interest in cargo drones by the commercial logistics sector will result in improvements in the near future. Search and rescue, mine clearance and fire-fighting are additional uses of drones that the report looks into’.
Mine clearance is of special interest to FSD. FSD's overarching aim is to alleviate and diminish the social, economic and environmental impacts of landmines and unexploded ordnance, thus creating favourable conditions for the reconstruction and development of war-torn countries.

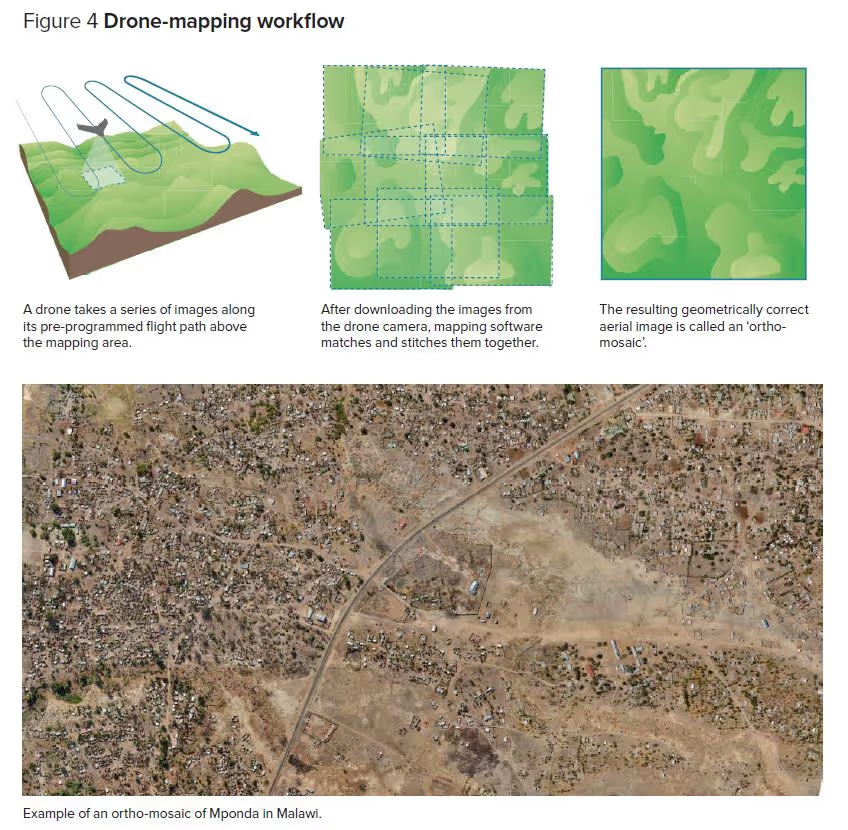
Traditionally mapping and monitoring have used satellite imaging, but drones can take photos that have 10 times as much detail as satellite images and in a manner that is both more transparent and more accessible to the community. Flight plans can be altered according to on-the-ground priorities and, being flown at low altitudes, drones can fly beneath cloud cover that often blocks the view from space.
Once drones have recorded detailed images of an area, experts can create maps that identify areas that are at high risk. These maps can then be shown to the local communities to discuss the risks are and how they might be addressed.
It seems we are someway off the much anticipated logistical application of drones. They simply are not yet sufficiently powerful to transport the tons of relief items that are typically needed during humanitarian emergencies.
Click here to enlarge the image below.
The use of drones has raised some major concerns relating to privacy, security and ethics. These are very much evolving issues, especially in a field dominated by military drones with their ability to provide surveillance and to destroy. Military use has led to a general distrust of how airbourne systems are used by governments. This makes operating in a way that gains the engagement and support of the local community even more critical. Audrey Lessard-Fontaine, project manager at CartONG commented:
‘We have generally found that local communities were very positive about the drones, but we have also seen that it is absolutely vital to involve them before and after the flights’.
CartONG is a French non-governmental organization committed to furthering the use of geographic information tools to improve data gathering and analysis for emergency relief and development programmes around the world.
The FSD report identified that, as drones become easier to use, the main challenges will shift from flying drones to processing, analysing and storing data that drones capture, which is one of the aspects of this HIF supported project.
A further illustration of the relevance of this project is the fact that ‘Drones frequently arrive too late to be useful in the immediate aftermath of a disaster. Organizations can address this issue by building local or regional capacity and integrating drones into their emergency response toolkits’. This highlights the potential value of a local aerial survey capacity for communities that are at risk, be it from flooding, landslides or even food security where local water resources need to be carefully managed.
Click here to enlarge the image below.
What are the lessons from this report?
- Focus on adding value to the proven mapping applications through data management and analytics.
- New applications will be constantly evolving.
- Empowering communities by training them to use drones as tools which may have day to day benefits and show them how this aerial survey capacity can increase their resilience in times of emergency.
- Ensure that new ideas and applications are grounded in real use cases.
Stay updated
Sign up for our newsletter to receive regular updates on resources, news, and insights like this. Don’t miss out on important information that can help you stay informed and engaged.
Related articles



Explore Elrha
Learn more about our mission, the organisations we support, and the resources we provide to drive research and innovation in humanitarian response.